Title: The Mirror of Literature, Amusement, and Instruction. Volume 14, No. 404, December 12, 1829
Author: Various
Release date: March 1, 2004 [eBook #11463]
Most recently updated: December 25, 2020
Language: English
Credits: E-text prepared by Jonathan Ingram, Andy Jewell, David Garcia, and the Project Gutenberg Online Distributed Proofreading Team
| VOL. XIV, NO. 404.] | SATURDAY, DECEMBER 12, 1829. | [PRICE 2d. |
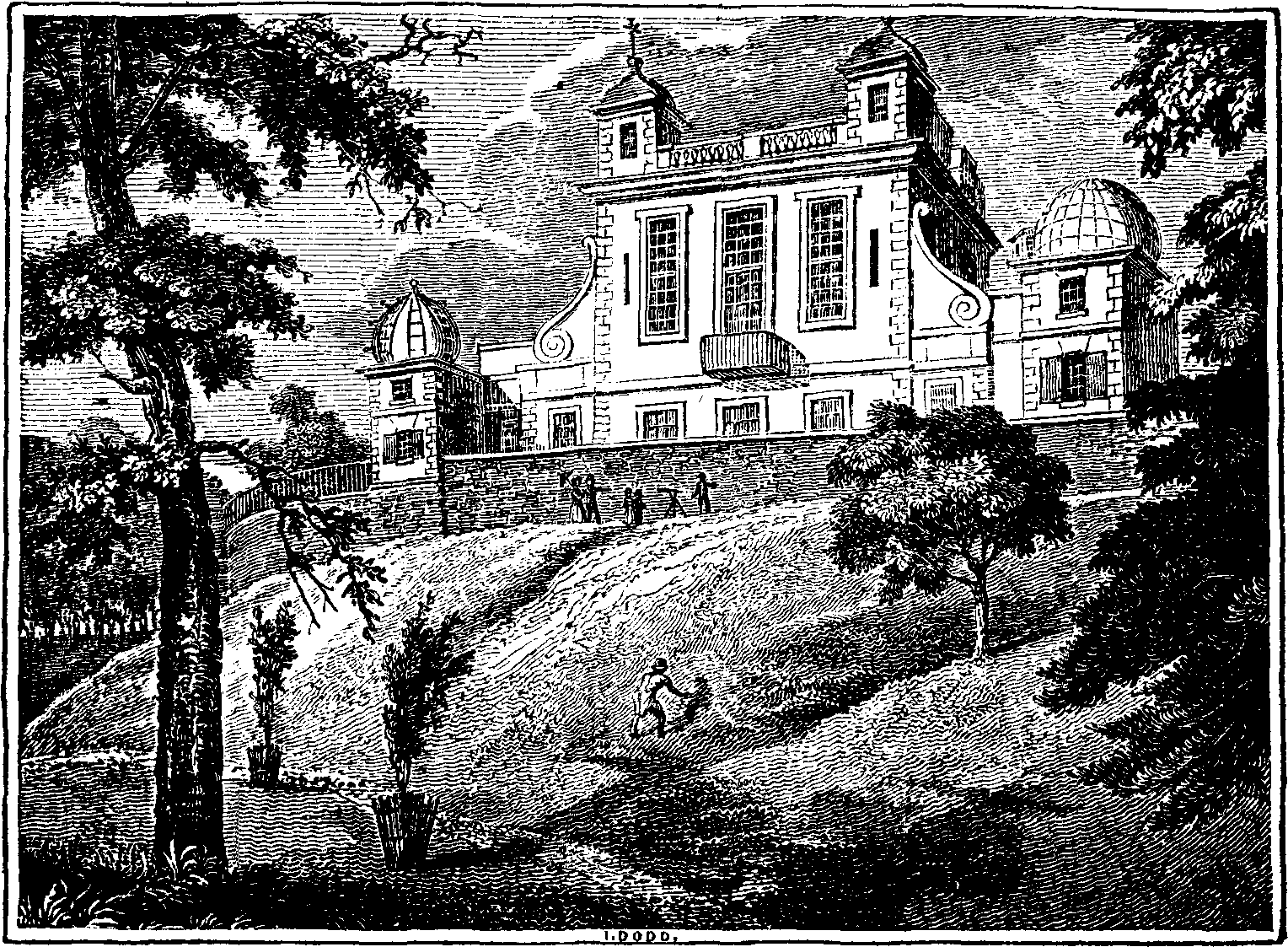
In the present almanack season, as it is technically called, the above illustration of our pages may not be inappropriate or ill-timed, inasmuch as it represents the spot whence all English astronomers make their calculations.
The Observatory was built by Charles II., in the year 1675—probably, observes a recent writer, "with no better motive than to imitate Louis XIV.," who had just completed the erection and endowment of an observatory at Paris. The English Observatory was fortunately placed under the direction of the celebrated Flamstead, whose name the hill, or site of the building, still retains. He was appointed astronomer-royal in 1676; but Charles (as in the case of the curious dial at Whitehall, described by us a few weeks since1), neglected to complete what he had so well begun: and Flamstead entered upon the duties of his appointment with instruments principally provided at his own expense, and that of a zealous patron of science, James Moore. It should seem that this species of parsimony is hereditary in the English Government, for, upon the authority of the Quarterly Review, we learn that "within the wide range of the British Islands there is only one observatory (Greenwich), and scarcely one supported by the Government. We say scarcely one, because we believe that some of the instruments in the observatory at Greenwich were purchased out of the private funds of the Royal Society of London."2
The first stone of this Observatory was laid by Flamstead, on the 10th of August, 1675. It stands 160 feet above low-water mark, and principally consists of two separate buildings: the first contains three rooms on the ground-floor—viz. the transit-room, towards the east, the quadrant-room, towards the west, and the assistant's sitting and calculating-room, in the middle; above which is his bed-room, the latter being furnished with sliding shutters in the roof. In [pg 402] the transit-room is an eight-feet transit-instrument, with an axis of three feet, resting on two piers of stone: this was made by Bird, but has been much improved by Dolland, Troughton, and others. Near it is a curious transit-clock, made by Graham, but greatly improved by Earnshaw, who so simplified the train as to exclude two or three wheels, and also added cross-braces to the gridiron-pendulum, by which an error of a second per day, arising from its sudden starts, was corrected. The quadrant-room has a stone pier in the middle, running north and south, having on its east face a mural-quadrant, of eight feet radius, made by Bird, in 1749, by which observations are made on the southern quarter of the meridian, through an opening in the roof three feet wide, produced by means of two sliding shutters; on its west face is another eight-feet mural quadrant, with an iron frame, and an arch of brass, made by Graham, in 1725: this is applied to the north quarter of the meridian. In the same apartment is the famous zenith-sector, twelve feet in length, with which Dr. Bradley, at Wanstead, and at Kew, made those observations which led to the discovery of the aberration and nutation: here also is Dr. Hooke's reflecting telescope, and three telescopes by Harrison. On the south side of this room is a small building, for observing the eclipses of Jupiter's satellites, occultations, &c., with sliding shutters at the roof and sides, to view any portion of the hemisphere, from the prime verticle down to the southern horizon: this contains a forty-inch achromatic, by the inventor, Mr. John Dolland, with a triple object-glass, a most perfect instrument of its kind; and a five-feet achromatic, by John and Peter Dolland, his sons. Here, likewise, are a two-feet reflecting-telescope (the metals of which were ground by the Rev. Mr. Edwards), and a six-feet reflector, by Dr. Herschell.
The lower part of the house serves merely for a habitation; but above is a large octagonal room, which, being now seldom wanted for astronomical purposes, is used as a repository for such instruments as are too large to be generally employed in the apartments first described, or for old instruments, which modern improvements have superseded. Among the former is a most excellent ten-feet achromatic, by the present Mr. Dolland, and a six-feet reflector, by Short, with a clock to be used with them. In the latter class, besides many curious and original articles, which are deposited in boxes and cupboards, is the first transit instrument that was, probably, ever made, having the telescope near one end of the axis; and two long telescopes with square wooden tubes, of very ancient date. Here, likewise, is the library, which is stored with scarce and curious old astronomical works, including Dr. Halley's original observations, and Captain Cook's Journals. Good busts of Flamstead and Newton, on pedestals, ornament this apartment; and in one corner is a dark narrow staircase, leading to the leads above, whence the prospect is uncommonly grand; and to render the pleasure more complete, there is, in the western turret, a camera obscura, of unrivalled excellence, by which all the surrounding objects, both movable and immovable, are beautifully represented in their own natural colours, on a concave table of plaster of Paris, about three feet in diameter.
On the north side of the Observatory are two small buildings, covered with hemispherical sliding domes, in each of which is an equatorial sector, made by Sisson, and a clock, by Arnold, with a three-barred pendulum, which are seldom used but for observing comets. The celebrated Dry-well, which was made to observe the earth's annual parallax, and for seeing the stars in the day-time, is situated near the south-east corner of the garden, behind the Observatory, but has been arched over, the great improvements in telescopes having long rendered it unnecesary. It contains a stone staircase, winding from the top to the bottom.
The Rev. John Flamstead, Dr. Halley, Dr. Bradley, Dr. Bliss, Dr. Nev. Maskelyne, and John Pond, Esq. have been the successive astronomers-royal since the foundation of this edifice.
(For the Mirror.)
The most extraordinary instance of this kind on record is that of the united twins, born at Saxony, in Hungary, in 1701; and publicly exhibited in many parts of Europe, among others in England, and living till 1723. They were joined at the back, below the loins, and had their faces and bodies placed half side-ways towards each other. They were not equally strong nor well made, and the most powerful, (for they had separate wills) dragged the other after her, when she wanted to go any where. At six years, one had [pg 403] a paralytic affection of the left side, which left her much weaker than the other. There was a great difference in their functions and health. They had different temperaments; when one was asleep the other was often awake; one had a desire for food when the other had not, &c. They had the small pox and measles at one and the same time, but other disorders separately. Judith was often convulsed, while Helen remained free from indisposition; one of them had a catarrh and a cholic, while the other was well. Their intellectual powers were different; they were brisk, merry, and well bred; they could read, write, and sing, very prettily; could speak several languages, as Hungarian, German, French, and English. They died together, and were buried in the Convent of the Nuns of St. Ursula, at Presburgh.
P.T.W.
(For the Mirror.)
Oh, mourn ye deities of love.
And ye whose minds distress can move,
Bewail a Sparrow's fate;
The Sparrow, favourite of my fair,
Fond object of her tend'rest care,
Her loss indeed how great.
For so affectionate it grew,
And its delighted mistress knew
As well as she her mother;
Nor would it e'er her lap forsake,
But hopping round about would make
Some sportive trick or other.
It now that gloomy road has pass'd.
That road which all must go at last,
From whence there's no retreat;
But evil to you, shades of death,
For having thus deprived of breath
A favourite so sweet.
Oh, shameful deed! oh, hapless bird!
My charmer, since its death occurr'd,
So many tears has shed,
That her dear eyes, through pain and grief,
And woe, admitting no relief,
Alas, are swoln and red.
T.C.
(For the Mirror.)
The following explanation of a few of the terms employed to designate parts of Gothic architecture, may, perhaps, prove acceptable to some of your readers. Having felt the need of such assistance in the course of my own reading, &c. &c.—I extracted them from an expensive work on the subject, and have only to lament that my vocabulary should be so defective.
Buttresses.—Projections between the windows and at the corners.
Corbel.—An ornamental projection from the wall to support an arch, niche, beam, or other apparent weight. It is often a head or part of a figure.
Bands.—Either small strings around shafts, or horizontal lines of square, round, and other formed panels, used to ornament spires, towers, and similar works.
Cornice.—The tablet at the top of a wall, running under the battlement. It becomes a
Basement when at the bottom of it, and beneath this the wall is generally thicker.
Battlement.—It may be indented or plain; sunk, panelled, or pierced.
Crockets.—Small bunches of foliage, ornamenting canopies and pinnacles.
Canopies.—Adorned drip-stones.—Vide Dripstone.
Crypts.—Vaulted chapels under some large churches, and a few small ones.
Crisps.—Small arches; sometimes double-feathered, and according to the number of them in immediate connexion; they are termed tre-foils, quatre-foils, cinque-foils, &c.
Dripstone.—The tablet running round doors and windows.
Featherings or Foliations.—Parts of tracery ornamented with small arches and points, are termed Feathered, or Foliated.
Finials.—Large crockets surmounting canopies and pinnacles. This term is frequently applied to the whole pinnacle.
Machicolations.—Projecting battlements, with intervals for discharging missiles on the heads of assailants.
Mullions.—By these, windows are divided into lights.
Parapet.—When walls are crowned with a parapet, it is straight at the top.
Pinnacle.—A small spire, generally four-sided, and placed on the top of buttresses, &c., both exterior and interior.
Piers.—Spaces in the interior of a building between the arches.
Rood Loft.—In ancient churches, not collegiate, a screen between the nave and chancel was so called, which had on the top of it a large projection, whereon were placed certain images, especially those which composed the rood.
Set-offs.—The mouldings and slopes dividing buttresses into stages.
Spandrells.—Spaces, either plain or [pg 404] ornamented, between an arch and the square formed round it.
Stoups.—The basins in niches, which held holy water. Near the altar in old churches, or where the altar has been, is sometimes found another niche, distinguished from the stoup, by having in it at the bottom, a small aperture for carrying off the water; it is often double with a place for bread.
Tabernacle-work.—Ornamented open work over stalls; and generally any minute ornamental open-work.
Tablets.—Small projecting mouldings or strings, mostly horizontal.
Tracery.—Ornaments of the division at the heads of windows. Flowing, when the lines branch out into flowers, leaves, arches, &c. Perpendicular, when the mullions are continued through the straight lines.
Transoms.—The horizontal divisions of windows and panelling.
Turrets.—Towers of great height in proportion to their diameter are so called. Large towers have often turrets at their corners; often one larger than the other, containing a staircase; and sometimes they have only that one.
The Norman—Commenced before the conquest, and continued until the reign of Henry II. A.D., 1189. It is characterized by semicircular, and sometimes pointed, arches, rudely ornamented.
Early English.—This style lasted until the reign of Edward I., A.D. 1307. Its characteristics are, pointed arches, long narrow windows, and the jagged or toothed ornament.
Decorated English—Lasted to the end of Edward III., A.D. 1377. It is characterized by large windows with pointed arches divided into many lights by mullions. The tracery of this style is in flowing lines, forming figures. It has many ornaments, light and delicately wrought.
Perpendicular English.—This last style employed latterly only in additions, was in use, though much debased, even as late as 1630-40. The latest whole building in it, is not later than Henry VIII. Its characteristics are the mullions of the windows, and ornamental panelings, run in perpendicular lines; and many buildings in this style are so crowded with ornament, that the beauty of the style is destroyed. The carvings of it are delicately executed.
M.L.B.
(For the Mirror.)
In the days of Caliph Haroun Alraschid, the neighbourhood of Bagdad was infested by a clan of banditti, known by the name of the "Ranger Band." Their rendezvous was known to be the forests and mountains; but their immediate retreat was a mystery time had not divulged.
That they were valiant, the intrepidity with which they attacked in the glare of noonday would demonstrate; that they were numerous, the many robberies carried on in the different parts of the Caliph's dominions would indicate; and that they were bloody, their invariable practice of killing their victim before they plundered him would argue. They had sworn by their Prophet never to betray one another, and by the Angel of Death to shed their blood in each other's defence. No wonder, then, that they were so difficult to be captured; and when taken, no tortures or promises of reward could extract from them any information as to the retreat of their comrades.
One day, as Giafar, the Vizier, and favourite of the Caliph, was walking alone in a public garden of the city, a stranger appeared, who, after prostrating himself before the second man in the empire, addressed him in these words: "High and mighty Vizier of Alraschid, Lord of the realms of Alla upon earth, whose delegate and vicegerent he is, hear the humblest of the sons of men—Vizier, hear me!"
"Speak, son," said the Vizier, "I am patient."
"And," continued the stranger, "what I have to communicate, be pleased to transmit to our gracious and well-beloved Caliph."
"Let me hear thy suit—it may be in my power to assist you," replied the Vizier.
"The beauteous Ada is in the clutches of ruffians," responded the stranger; "and"—
"Well," said the Vizier, "proceed."
"To be brief, the forest bandit snatched her from my arms—we were betrothed. I have applied to a mighty enchanter, the Genius of the Dale, who tells me she is still living, and in the cavern of the bandit—that her beauty and innocence melted the hearts of robbers, and that were they not afraid of [pg 405] their haunt being discovered, they would have restored her to liberty; but where that cavern is was beyond his power to tell. However, he has informed me how I may demand and obtain the assistance of a much more powerful enchanter than himself; but that genius being the help of Muloch, the Spirit of the Mountain, I need the aid of the Caliph himself. May it please the highness of mighty Giafar to bend before the majesty of the Sovereign of the East, and supplicate in behalf of thy servant Abad."
"How," said the Vizier, "can the Caliph be of service to thee?"
"It is requisite," replied the stranger, "that my hand be stained with the blood of the Caliph, before I summon this most mighty fiend!"—
"How!" cried the astonished Vizier, "would'st thou shed the blood of our beloved master?—No, by Alla!"—
"Pardon me," rejoined the stranger, interrupting him, "and Heaven avert that any thought of harm against the father of his people should warm the breast of Abad; I wish only to anoint my finger with as much of his precious blood as would hide the point of the finest needle; and should this most inestimable favour be conferred upon me, I undertake, under pain of suffering all the tortures that human ingenuity can devise, or devilish vengeance inflict, to exterminate the hated race of banditti who now infest the forests of the East."
"Son," said the aged Vizier, "I will plead thy cause; meet me here on the morrow, and in the mean time consider thy request as granted."
"Father, I take my leave; and may the Guardian of the Good shower down a thousand blessings on thy head!"
Abad made a profound obeisance to the Vizier, and they separated: the latter to conduct the affairs of the state, and the former to toil through the more menial labours of the day.
Morning came; Abad was at the appointed spot before sunrise, and waited with impatience for the expected hour when the Vizier was to arrive. The Vizier was punctual; and with him, in a plain habit, was the Caliph himself, who underwent the operation of having blood drawn from him by the hand of Abad.
At midnight, Abad, as he had been directed by the Genius of the Dale, went to the cave of the Spirit of the Mountain. He was alone! It was pitchy dark; the winds howled through the thick foliage of the forest; the owls shrieked, and the wolves bayed; the loneliness of the place was calculated to inspire terror! and the idea of meeting such a personage, at such an hour, did not contribute to the removal of that terror! He trembled most violently. At length, summoning up courage he entered the mystic cell, and commenced challenging the assistance of the Spirit of the Mountain in the following words:
"In the name of the Genius of the Dale I conjure you! by our holy Prophet I command you! by the darkness of this murky night I entreat you! and by the blood of a Caliph, shed by this weak arm, I allure you, most potent Muloch, to appear! Muloch rise! help! appear!"
At this instant the monster appeared, in the form of a human being of gigantic stature and proportions, having a fierce aspect, large, dark, rolling eyes, bushy eyebrows, and a thick black beard—attired in the habit of a blacksmith! He bore a huge hammer in his right hand, and in his left he carried a pair of pincers, in which was grasped a piece of shapeless metal. His eyes flashed with indignation as he flourished the ponderous hammer over his head, as though it had been a small sword—when, striking the metal he held in the forceps, a round, well-formed shield fell from the stroke.
"Mortal!" vociferated the enchanter, in a voice of thunder, "there is thy weapon and defence!"—flinging the weighty hammer on the ample shield, the collision of which produced a sound in unison with the deep bass of Muloch's voice; nor did the reverberation that succeeded cease to ring in the ears of Abad until several minutes after the spectre had disappeared.
Abad rejoiced when the fearful visit was over, and, well pleased with his success, was preparing to depart; but his joy was damped on finding the hammer so heavy that he could not, without difficulty, remove it from off the shield. He left it in the cave, and returned with the shield only, comforting himself that however he might be at a loss for a weapon, he had a shield that would render him invincible.
His next care was to discover the retreat of the robbers, otherwise he was waging a war with shadows. After making every inquiry, and wandering in vain for several months in quest of them, he was not able to obtain a glimpse of the objects of his search. Still they seemed to possess ubiquity. Their depredations continued, murders multiplied, and their attacks became more open and formidable. Missions were sent daily to the royal city from the [pg 406] emirs and governors of provinces residing at a distance with the most lamentable accounts, and soldiers were dispatched in large bodies to scour the country, but all was of no avail.
Abad had almost abandoned himself to despair, when, one lovely evening, as he wandered along the banks of the Tigris, he observed a boat, laden with armed men, sailing rapidly down the river. "These must be a party of the ranger band. Oh, Mahomet!" said he, prostrating himself on the earth, "be thou my guide!" At length the crew landed on the opposite shore, which was a continued series of crags, and fastening a chain attached to the boat to a staple driven into the rock, under the surface of the water, they suffered the vessel to float with the stream beneath the overhanging rocks, which afforded a convenient shelter and hiding place for it, as it was impossible for any one passing up or down the river to notice it.
Having landed, the party ascended the acclivity, when, suddenly halting and looking round, to ascertain that they were not observed, they removed a large rolling stone that blockaded the entrance, and went into what appeared a natural cavern, then closing the inlet. Not a vestige of them remained in sight, and nature seemed to reign alone amidst the sublimest of her works.
Hope again glowed in the breast of Abad; he soon found means for crossing the stream, and marched boldly to the very entrance of the robber's cave, and with all his might attempted to roll the stone from its axis. But here he was again doomed to disappointment: without the possession of the talisman, kept by the captain of the band, he might as well have attempted to roll the mountain on which he stood into the water beneath, as to have shifted the massy portal: the strength of ten thousand men, could their united efforts have been made available at one and the same time, would not have been sufficient even to stir it.
Abad was returning, disappointed and murmuring at his fate, when he bethought himself of the hammer which Muloch, the Spirit of the Mountain, had promised should be of such powerful aid. He hastened to the place where he had left the large instrument, and the next day brought it to the robbers' cave. He was in the act of lifting the massive weight, to have shattered the adamantine stoppage, when he was surprised by a noise behind him. He looked, and saw the banditti trooping up the ravine: they were returning, on horseback, from an expedition of plunder, laden with conquest. Abad hastily, to avoid discovery, struck the large stone with the charmed hammer, when it receded from the blow and, admitting him into the cave, closed itself upon him. The bandit chief, on seeing a stranger enter, ordered his men to advance rapidly up the ravine, which leads from the waters of the Tigris to the very threshold of the cave, embosomed amidst gigantic and stately rocks.
The captain in vain applied the magic talisman to the charmed stone; the more potent shield of Muloch was within. Enraged at being thus thwarted, he demanded admittance. Abad made no reply, but, raising the enchanted hammer against the ponderous bulwark with his whole strength (and he felt as though gifted with more than mortal strength), he, at one tremendous blow, dislodged the stone which had stood at the entrance of the cave, amidst the shock of tempests and the convulsions of nature, from the creation of the world—as hard as adamant, heavy as gold, and as round as the balls on the cupolas of Bagdad. The bulk rolled down the ravine, bearing with it trees and fragments of rock; men and horses, and all meaner obstructions, were crushed to atoms beneath its weight, as it thundered down the sloping track, and occasionally fell over the steep precipices, which only served to increase its velocity! nor did it stop in its headlong career until it had annihilated the whole of the ranger band, and disappeared amidst the boiling foam of the angry Tigris!
Abad, wrapt in wonder, cast his eyes on the earth, to view the terrific instrument with which he had performed so wonderful an exploit; but, to add more to his astonishment, the hammer and shield had vanished!
Curiosity, and the hope of meeting his betrothed, now led him to explore the winding recesses of the mystic cavern, which consisted of numerous archways—some artificial, others, the natural formation of subterranean rocks, leading to a large apartment, in which were deposited the spoils which a century of plunder had contributed to accumulate. Whilst feasting his eyes on the rich piles of jewellery, and reviewing the bags of gold which everywhere presented themselves, his eyes met the features of a female. He could not be mistaken—he looked again as she advanced nearer the light—it was the beauteous Ada, still young and lovely! Bagdad did not possess such a maiden, [pg 407] nor did poet ever paint a fairer form! Abad thought her nothing inferior to the Houris of Paradise. She fulfilled every expectation through a long and virtuous life, during which time they enjoyed the ill-gotten wealth of the ranger band; and, although the splendour of their living was exceeded only by that of the Caliph's, they were bountiful to their dependents: they built an asylum for the destitute—were universally beloved and respected—and their magnificence was only surpassed by their benevolence!
CYMBELINE.
Shame sticks ever close to the ribs of honour,
Great men are never found after it:
It leaves some ache or other in their names still,
Which their posterity feels at ev'ry weather.
MIDDLETON.
From damned deeds abstain,
From lawless riots and from pleasure's vain;
If not regarding of thy own degree,
Yet in behalf of thy posterity.
For we are docible to imitate.
Depraved pleasures though degenerate.
Be careful therefore least thy son admit
By ear or eye things filthy or unfit.
LODGE.
Shame follows sin, disgrace is daily given,
Impiety will out, never so closely done,
No walls can hide us from the eye of heaven,
For shame must end what wickedness begun,
Forth breaks reproach when we least think thereon.
DANIELL.
A wise man poor
Is like a sacred book that's never read,
T' himself he lives, and to all else seems dead.
This age thinks better of a gilded fool,
Than of thread-bare saint in Wisdom's school
DEKKAR.
She was a woman in the freshest age,
Of wondrous beauty, and of bounty rare,
With goodly grace, and comely personage.
That was on earth not easy to compare,
Full of great love; but Cupid's wanton snare
As hell she hated, chaste in work and will,
Her neck and breast were ever open bare,
That aye thereof her babes might suck their fill,
The rest was all in yellow robes arrayed still,
A multitude of babes about her hung,
Playing their sports that joyed her to behold,
Whom still she fed, while they were weak and young,
But thrust them forth still as they waxed old,
And on her head she wore a tire of gold;
Adorn'd with gems and ouches fair,
Whose passing price unneath was to be told,
And by her side there sat a gentle pair
Of turtle-doves, she sitting in an ivory chair.
SPENSER.
It is a work of Charity God knows,
The reconcilement of two mortal foes.
MIDDLETON.
When the air is calm and still, as dead and deaf
And under heaven quakes not an aspen leaf:
When seas are calm and thousand vessels fleet
Upon the sleeping seas with passage sweet;
And when the variant wind is still and lone
The cunning pilot never can be known:
But when the cruel storm doth threat the bark
To drown in deeps of pits infernal dark,
While tossing tears both rudder, mast, and sail,
While mounting, seems the azure skies to scale,
While drives perforce upon some deadly shore,
There is the pilot known, and not before.
T. HUDSON.
The knotty oak and wainscot old,
Within doth eat the silly worm:
Even so a mind in envy cold,
Always within itself doth burn.
FITZ JEFFRY.
Opinion is as various as light change,
Now speaking courtlike, friendly, straight as strange,
She's any humour's perfect parasite,
Displeas'd with her, and pleas'd with her delight.
She is the echo of inconstancy,
Soothing her no with nay, her ay with yea.
GUILPIN.
Happy is he that lives in such a sort
That need not fear the tongues of false report.
EARL OF SURREY.
By care lay heavy Sleep the cousin of Death,
Flat on the ground, and still as any stone;
A very corpse, save yielding forth a breath,
Small keep took he whom Fortune frown'd on,
Or whom she lifted up into a throne
Of high renown; but as a living death
So dead alive, of life he drew the breath.
SACKVILLE.
War the mistress of enormity,
Mother of mischief, monster of deformity,
Laws, manners, arts, she breaks, she mars, she chases,
Blood, tears, bowers, towers, she spills, smites, burns, and rases,
Her brazen teeth shake all the earth asunder;
Her mouth a fire brand, her voice is thunder;
Her looks are lightning, every glance a flash,
Her fingers guns, that all to powder plash,
Fear and despair, flight and disorder, coast
With hasty march before her murderous host,
As burning, rape, waste, wrong, impiety,
Rage, ruin, discord, horror, cruelty,
Sack, sacrilege, impunity, pride.
Are still stern consorts by her barbarous side;
And poverty, sorrow, and desolation,
Follow her army's bloody transmigration.
SYLVESTER.
Of all chaste birds the phoenix doth excel,
Of all strong beasts the lion bears the bell,
Of all sweet flowers the rose doth sweetest smell.
Of all pure metals gold is only purest,
Of all the trees the pine hath highest crest.
Of all proud birds the eagle pleaseth Jove,
Of pretty fowls kind Venus likes the dove,
Of trees Minerva doth the olive move.
LODGE.
The frequent mention of the Cochineal Insect and Plant in our pages will, probably, render the annexed cut of more than ordinary interest to our readers.3
The plant on which the Cochineal Insect is found, is called the Nopal, a species of Opuntia, or Prickly Pear, which abounds on all the coasts of the Mediterranean; and is thus described by Mr. Thompson, in his work entitled, Official Visit to Guatemala; "The nopal is a plant consisting of little stems, but expanding itself into wide, thick leaves, more or less prickly according to its different kind: one or two of these leaves being set as one plant, at the distance of two or three feet square from each other, are inoculated with the cochineal, which, I scarcely need say, is an insect; it is the same as if you would take the blight off an apple or other common tree, and rub a small portion of it on another tree free from the contagion, when the consequence would be, that the tree so inoculated would become covered with the blight; a small quantity of the insects in question is sufficient for each plant, which in proportion as it increases its leaves, is sure to be covered with this costly parasite. When the plant is perfectly saturated, the cochineal is scraped off with great care. The plants are not very valuable for the first year, but they may be estimated as yielding after the second year, from a dollar and a half profit on each plant."
The insect is famous for the fine scarlet dye which it communicates to wool and silk. The females yield the best colour, and are in number to the males as three hundred to one. Cochineal was at first supposed to be a grain, which name it retains by way of eminence among dyers, but naturalists soon discovered it to be an insect. Its present importance in dyeing is an excellent illustration of chemistry applied to the arts; for long after its introduction, it gave but a dull kind of crimson, till a chemist named Kuster, who settled at Bow, near London, about the middle of the sixteenth century, discovered the use of the solution of tin, and the means of preparing with it and cochineal, a durable and beautiful scarlet.
Fine cochineal, which has been well dried and properly kept, ought to be of a grey colour inclining to purple. The grey is owing to a powder which covers it naturally, a part of which it still retains; the purple tinge proceeds from the colour extracted by the water in which it has been killed. Cochineal will keep a long time in a dry place. Hellot says, that he tried some one hundred and thirty years old, and found it produce the same effect as new.
There is now in the neigbourhood of Dovercourt, in Essex, upon the estate of Sir T. Gaisford, a chestnut-tree fifty-six feet in circumference, which flourishes well, and has had a very good crop of chestnuts for many years.
J.T.
I'd be an Alderman, born in the City,
Where haunches of venison and green turtles meet
Seeking in Leadenliall, reckless of pity,
Birds, beast, and fish, that the knowing ones eat
I'd never languish for want of a luncheon.
I'd never grieve for the want of a treat;
I'd be an Alderman, constantly munching,
Where haunches of venison and green turtles meet.
Oh! could I wheedle the votes at the vestry,
I'd have a share of those good sav'ry things;
Enchained by turkey, in love with the pastry.
And floating in Champagne, while Bow bells ring.
Those who are cautious are skinny and fretful,
Hunger, alas! naught but ill-humour brings;
I'd be an Alderman, rich with a net full,
Rolling in Guildhall, whilst old Bow bells ring.
What though you tell me that prompt apoplexy
Grins o'er the glories of Lord Mayor's Day,
'Tis better, my boy, than blue devils to vex ye,
Or ling'ring consumption to gnaw you away.
Some in their folly take black-draught and blue-pill,
And ask ABERNETHY their fate to delay;
I'd he an Alderman, WAITHMAN'S apt pupil,
Failing when dinner things are clearing away.
Monthly Magazine.
I once resided in a country town; I will not specify whether that town was Devizes or Doncaster, Beverley or Brighton: I think it highly reprehensible in a writer to be personal, and scarcely more venial do I consider the fault of him who presumes to be local. I will, however, state, that my residence lay among the manufacturing districts; but lest any of my readers should be misled by that avowal, I must inform them, that in my estimation all country towns, from the elegant Bath, down to the laborious Bristol, are (whatever their respective polite or mercantile inhabitants may say to the contrary), positively, comparatively, and superlatively, manufacturing towns!
Club-rooms, ball-rooms, card-tables, and confectioners' shops, are the factories; and gossips, both male and female, are the labouring classes. Norwich boasts of the durability of her stuffs; the manufacturers I allude to weave a web more flimsy. The stuff of tomorrow will seldom be the same that is publicly worn to-day; and were it not for the zeal and assiduity of the labourers, we should want novelties to replace the stuff that is worn out hour by hour.
No man or woman who ever ventures to deviate from the beaten track should ever live in a country town. The gossips all turn from the task of nibbling one another, and the character of the lusus naturae becomes public property. I am the mother of a family, and I am known to have written romances. My husband, in an evil hour, took a fancy to a house at a watering-place, which, by way of distinction, I shall designate by the appellation of Pumpington Wells: there we established ourselves in the year 1800.
The manufacturers received us with a great show of civility, exhibiting to us the most recent stuff, and discussing the merits of the newest fabrications. We, however, were not used to trouble ourselves about matters that did not concern us, and we soon offended them.
We turned a deaf ear to all evil communications. If we were told that Mr. A., "though fond of show, starved his servants," we replied, we did not wish to listen to the tale. If we heard that Mr. B. though uxorious in public, was known to beat his wife in private, we cared not for the matrimonial anecdote. When maiden ladies assured us that Mrs. C. cheated at cards, we smiled, for we had no dealings with her; and when we were told that Mrs. D. never paid her bills, we repeated not the account to the next person we met; for as we were not her creditors, her accounts concerned us not.
We settled ourselves, much to our satisfaction, in our provincial abode: it was a watering-place, which my husband, as a bachelor, had frequented during its annual season.
As a watering-place he knew it well. Such places are vastly entertaining to visiters, having no "local habitation," and no "name"—caring not for the politics of the place, and where, if any thing displeases them, they may pay for their lodgings, order post-horses, and never suffer their names to appear in the arrival book again.
But with those who live at watering-places, it is quite another affair. For the first six months we were deemed a great acquisition. There were two or three sets in Pumpington Wells—the good, the bad, and the indifferent. The bad left their cards, and asked us to dances, the week we arrived; the indifferent knocked at our door in the first month; and even before the end of the second, we were on the visiting lists of the good. We knew enough of society to be aware that it is impolitic to rush into the embraces of all the arms that are extended to receive strangers; but feeling no wish to affront any one in return for an intended civility, we gave card for card; and the doors of good, bad, and indifferent, received our names.
All seemed to infer, that the amicable gauntlet, which had been thrown down, having been courteously taken up, the ungloved hands were forthwith to be grasped in token of good fellowship; we had left our names for them, and by the invitations that poured in upon us, they seemed to say with Juliet—
"And for thy name, which is no part of thee,
Take all myself."
No man, not even a provincial, can visit every body; and it seems but fair, that if a selection is to be made, all should interchange the hospitalities of [pg 410] life with those persons in whose society they feel the greatest enjoyment.
Many a dinner, therefore, did we decline—many a route did we reject; my husband's popularity tottered, and the inviters, though they no longer dinned their dinners in our ears, and teazed us with their "teas," vowed secret vengeance, and muttered "curses, not loud, but deep."
I have hinted that we had no scandalous capabilities; and though slander flashed around us, we seldom admitted morning visiters, and our street-door was a non-conductor.
But our next door neighbours were maiden ladies, who had been younger, and, to use a common term of commiseration, had seen better days—by which, I mean the days of bloom, natural hair, partners, and the probability of husbands.
Their vicinity to us was an infinite comfort to the town, for those who were unable to gain admittance at our door to disturb our business and desires,
"For every man has business and desire,
Such as they are,"
were certain of better success at our neighbours', where they at least could gain some information about us "from eye-witnesses who resided on the spot."
My sins were numbered, so were my new bonnets; and for a time my husband was pitied, because "he had an extravagant wife;" but when it was ascertained that his plate was handsome, his dinner satisfactory in its removes, and comme il faut in its courses, those whose feet had never been within our door, saw clearly "how it must all end, and really felt for our trades-people."
I have acknowledged that I had written romances; the occupation was to me a source of amusement; and as I had been successful, my husband saw no reason why he should discourage me. A scribbling fool, in or out of petticoats, should be forbidden the use of pen, ink, and paper; but my husband had too much sense to heed the vulgar cry of "blue stocking." After a busy month passed in London, we saw my new novel sent forth to the public, and then returned to our mansion at Pumpington Wells.
As we drove up to our door, our virgin neighbours gazed on us, if possible, with more than their former interest. They wiped their spectacles; with glances of commiseration they saw us alight, and with unwearied scrutiny they witnessed the removal of our luggage from the carriage. We went out—every body stared at us—the people we did know touched the hands we extended, and hastened on as if fearful of infection; the people we did not know whispered as they passed us, and looked back afterwards; the men servants seemed full of mysterious flurry when we left our cards at the doors of acquaintances, and the maid-servants peeped at us up the areas; the shopkeepers came from their counters to watch us down the streets—and all was whispering and wonder.
I could not make it out; was it to see the authoress? No; I had been an authoress when they last saw me. Was it the brilliant success of my new work? It could be nothing else.
My husband met a maiden lady, and bowed to her; she passed on without deigning to notice him. I spoke to an insipid man who had always bored me with his unprofitable intimacy, and he looked another way! The next lady we noticed tossed her head, as if she longed to toss it at us; and the next man we met opened his eyes astonishingly wide, and said—
"Are you here! Dear me! I was told you could not show your—I mean, did not mean to return!"
There was evidently some mystery, and we determined to wait patiently for its developement. "If," said I, "it bodes us good, time will unravel it." "And if," said my husband, "it bodes us evil, some d—d good-natured friend will tell us all about it."
We had friends at Pumpington Wells, and good ones too, but no friend enlightened us; that task devolved upon an acquaintance, a little slim elderly man, so frivolous and so garrulous, that he only wanted a turban, some rouge, and a red satin gown, to become the most perfect of old women.
He shook his head simultaneously as he shook our hands, and his little grey eyes twinkled with delight, while he professed to feel for us both the deepest commiseration.
"You are cut," said he; "its all up with you in Pumpington Wells."
"Pray be explicit," said I faintly, and dreading some cruel calumny, or plot against my peace.
"You've done the most impolitic thing! the most hazardous"—
"Sir!" said my husband, grasping his cane.
"I lament it," said the little man, turning to me; "your book has done it for you."
I thought of the reviews, and trembled.
"How could you," continued our tormentor, [pg 411] "how could you put the Pumpington Wells people in your novel?"
"The Pumpington Wells people!—Nonsense; there are good and bad people in my novel, and there are good and bad people in Pumpington Wells; but you flatter the good, if you think that when I dipped my pen in praise, I limited my sketches to the virtuous of this place; and what is worse, you libel the bad if you assert that my sketches of vice were meant personally to apply to the vicious who reside here."
"I libel—I assert!" said the old lady-like little man; "not I!—every body says so!"
"You may laugh," replied my mentor and tormentor combined, "but personality can be proved against you; and all the friends and relations of Mr. Flaw declare you meant the bad man of your book for him."
"His friends and relations are too kind to him."
"Then you have an irregular character in your book, and Mrs. Blemish's extensive circle of intimates assert that nothing can be more pointed than your allusion to her conduct and her character."
"And pray what do these persons say about it themselves?"
"They are outrageous, and go about the town absolutely wild."
"Fitting the caps on themselves?"
The little scarecrow shook his head once more; and declaring that we should see he had spoken too true, departed, and then lamented so fluently to every body the certainty of our being cut, that every body began to believe him.
I have hinted that my bonnets and my husband's plate occasioned heartburnings: no—that is not a correct term, the heart has nothing to do with such exhalations—bile collects elsewhere.
Those who had conspired to pull my husband from the throne of his popularity, because their parties excited in us no party spirit, and we abstained from hopping at their hops, found, to their consternation, that when the novelty of my novel misdemeanour was at an end, we went on as if nothing had occurred. However, they still possessed heaven's best gift, the use of their tongues, they said of us everything bad which they knew to be false, and which they wished to see realized.
Their forlorn hope was our "extravagance." "Never mind," said one, "Christmas must come round, and then we shall see."
When once the match of insinuation is applied to the train of rumoured difficulties, the suspicion that has been smouldering for awhile bounces at once into a report, and very shortly its echo is bounced in every parlour in a provincial town.
Long bills, that had been accustomed to wait for payment until Christmas, now lay on my table at midsummer; and tradesmen, who drove dennetts to cottages once every evening, sent short civil notes, regretting their utter inability to make up a sum of money by Saturday night, unless I favoured them, by the bearer, with the sum of ten pounds, "the amount of my little account."
Dennett-driving drapers actually threatened to fail for the want of ten pounds!—pastry-cooks, who took their families regularly "to summer at the sea," assisted the counter-plot, and prematurely dunned my husband!
It is not always convenient to pay sums at midsummer, which we had been in the habit of paying at Christmas; if, however, a single applicant was refused, a new rumour of inability was started and hunted through the town before night. People walked by our house, looking up wistfully at the windows; others peeped down the area, to see what we had for dinner. One gentleman went to our butcher, to inquire how much we owed him; and one lady narrowly escaped a legal action, because when she saw a few pipkins lying on the counter of a crockery-ware man, directed to me, she incautiously said, in the hearing of one of my servants, "Are you paid for your pipkins?—ah, it's well if you ever get your money!"
Christmas came at last; bills were paid, and my husband did not owe a shilling in Pumpington Wells. Like the old ladies in the besieged city, the gossips looked at us, wondering when the havoc would begin.
Ho who mounts the ladder of life, treading step by step upon the identical footings marked out, may live in a provincial town. When we want to drink spa waters, or vary the scene, we now visit watering-places; but rather than force me to live at one again, "stick me up," as Andrew Fairservice says, in Rob Roy, "as a regimental target for ball-practice." We have long ceased to live in Pumpington.
Fleeting are the tints of the rainbow—perishable the leaf of the rose—variable the love of woman—uncertain the sunbeam of April; but naught on earth can be fleeting; so perishable, so variable, or so uncertain, as the popularity of a provincial reputation.
Monthly Magazine.
Jack Jones was a toper: they say that some how
He'd a foot always ready to kick up a row;
And, when half-seas over, a quarrel he pick'd,
To keep up the row he had previously kick'd.
He spent all, then borrow'd at twenty per cent.
His mistress fought shy when his money was spent,
So he went for a soldier; he could not do less,
And scorn'd his fair Fanny for hugging brown Bess.
"Halt—Wheel into line!" and "Attention—Eyes right!"
Put Bacchus, and Venus, and Momus to flight
But who can depict half the sorrows he felt
When he dyed his mustachios and pipe-clay'd his belt?
When Sergeant Rattan, at Aurora's red peep,
Awaken'd his tyros by bawling—"Two deep!"
Jack Jones would retort, with a half-suppress'd sigh,
"Ay! too deep by half for such ninnies as I."
Quoth Jones—"'Twas delightful the bushes to beat
With a gun in my hand and a dog at my feet,
But the game at the Horse-Guards is different, good lack!
Tis a gun in my hand and a cat at my back."
To Bacchus, his saint, our dejected recruit.
One morn, about drill time, thus proffer'd his suit—
"Oh make me a sparrow, a wasp, or an ape—
All's one, so I get at the juice of the grape."
The God was propitious—he instantly found
His ten toes distend and take root in the ground;
His back was a stem, and his belly was bark,
And his hair in green leaves overshadow'd the Park.
Grapes clustering hung o'er his grenadier cap,
His blood became juice, and his marrow was sap:
Till nothing was left of the muscles and bones
That form'd the identical toper, Jack Jones.
Transform'd to a vine, he is still seen on guard,
At his former emporium in Great Scotland-yard;
And still, though a vine, like his fellow-recruits,
He is train'd, after listing, his ten-drills, and shoots.
New Monthly Magazine.
Edited by Mr. Thomas Roscoe, and dedicated to Professor Wilson, is no less attractive than its "Juvenile" rivals. Indeed, a few of the tales take a higher range than either of theirs,—as the Children's Island, an interesting Story, from the French of Madame Genlis; the Ball Dress; the Snow Storm; and the Deserted Village. The Heir of Newton Buzzard, a Tale in four cantos, by the late Mrs. John Hunter, is perhaps one of the prettiest juvenile novelties of the season. It is divided into Infancy—Childhood—Boyhood—and Youth—all which contain much amusement and moral point without dulness. We have not room for an entire story, but select one of Miss Mitford's village portraits:
"Dash was as beautiful a dog as eyes could be set on; one of the large old English Spaniels which are now so rare, with a superb head, like those which you see in Spanish pictures, and such ears! they more than met over his pretty spotted nose; and when he lapped his milk, dipped into the pan at least two inches. His hair was long and shiny and wavy, not curly, partly of a rich dark liver colour, partly of a silvery white, and beautifully feathered about the thighs and legs. He was extremely lively and intelligent, and had a sort of circular motion, a way of flinging himself quite round on his hind feet, something after the fashion in which the French dancers twist themselves round on one leg, which not only showed unusual agility in a dog of his size, but gave token of the same spirit and animation which sparkled in his bright hazel eye. Anything of eagerness or impatience was sure to excite this motion, and George Dinely gravely assured his sisters, when they at length joined him in the hall, that Dash had flung himself round six and twenty times whilst waiting the conclusion of their quarrel.
"Getting into the lawn and the open air did not tend to diminish Dash's glee or his capers, and the young party walked merrily on; George telling of school pranks and school misfortunes—the having lost or spoilt four hats since Easter, seemed rather to belong to the first class of adventures than the second—his sisters listening dutifully and wonderingly; and Dash, following his own devices, now turning up a mouse's nest from a water furrow in the park—now springing a covey of young partridges in a corn field—now plunging his whole hairy person in the brook; and now splashing Miss Helen from head to foot? by ungallantly jumping over her whilst crossing a stile, being thereunto prompted by a whistle from his young master, who had, with equal want of gallantry, leapt the stile first himself, and left his sisters to get over as they could; until at last the whole party, having passed the stile, and crossed the bridge, and turned the churchyard corner, found themselves in the shady recesses of the vicarage-lane, and in full view of the vine-covered cottage of Nurse Simmons."
Our closing extract is from "Anecdotes of South African Baboons," by Thomas Pringle, Esq.:
"It is the practice of these animals to descend from their rocky fastnesses in order to enjoy themselves on the banks of the mountain rivulets, and to feed on the nutritious bulbs which grow in the fertile valley ground. While thus occupied, they generally take care to be within reach of a steep crag, or precipice, to which they may fly for refuge on the appearance of an enemy; and one of their number is always placed as a sentinel on some large stone, or other prominent position, in order to give timely warning to the rest, of the approach of danger. It has frequently been my lot, when riding through the secluded valleys of that country, to come suddenly, on turning a corner of a wild glen, upon a troop of forty or fifty baboons thus quietly congregated. Instantly on my appearance, a loud cry of alarm being raised by the sentinel, the whole tribe would scamper off with precipitation; splashing through the stream, and then scrambling with most marvellous agility up the opposite cliffs, often several hundred feet in height, and where no other creature without wings, certainly, could attempt to follow them; the large males bringing up the rear-guard, ready to turn with fury upon the dogs, if any attempted to molest them; the females, with their young ones in their arms, or on their shoulders, clinging with arms clasped closely round the mothers' necks. And thus climbing, and chattering, and squalling, they would ascend the almost perpendicular crags, while I looked on and watched them—interested by the almost human affection which they evinced for their mates and their offspring; and sometimes not a little amused, also, by the angry vociferation with which the old ones would scold me when they had got fairly upon the rocks, and felt themselves secure from pursuit."
There are Seven Plates and a Vignette, and a glazed, ornamented cover which will withstand the wear and tear of the little play or book-room.
(Concluded from page 396.)
In the manufacture of a razor, it proceeds through a dozen hands; but it is afterwards submitted to a process of grinding, by which the concavity is perfected, and the fine edge produced. They are made from 1 s. per dozen, to 20 s. per razor, in which last the handle is valued at 16s.6d.
"Scissors, in like manner, are made by hand, and every pair passes through sixteen or seventeen hands, including fifty or sixty operations, before they are ready for sale. Common scissors are cast, and when riveted, are sold as low as 4s. 6d. per gross! Small pocket knives, too, are cast, both in blades and handles, and sold at 6 s. per gross, or a halfpenny each! These low articles are exported in vast quantities in casks to all parts of the world.
"Snuffers and trays are also articles of extensive production, and the latter are ornamented with landscapes, etched by a Sheffield artist, on a resinous varnish, and finished by being dipped in diluted nitric acid for a few seconds or minutes.
"Messrs. Rodgers also introduced me to an extensive range of workshops for the manufacture of plated and silver ware, in which are produced the most superb breakfast and dinner services. The method of making the silver plate here and at Birmingham merits special notice, because the ancient method was by dissolving mercury in nitrous acid, dipping the copper, and depending on the affinity of the metals, by which a very slight article was produced. But at Sheffield and Birmingham, all plate is now produced by rolling ingots of copper and silver together. About the eighth of an inch in thickness of silver is united by heat to an inch of copper in ingots about the size of a brick. It is then flattened by steel rollers worked by an eighty horse power. The greater malleability of the silver occasions it to spread equally with the copper into a sheet of any required thickness, according to the nature of the article for which it is wanted. I saw some pieces of plated metal, the eighth of an inch thick, rolled by hand into ten times their surface, the silver spreading equally; and I was told that the plating would be perfect if the rolling had reduced it to the thinness of silver paper! This mode of plating secures to modern plate a durability not possessed by any plate silvered by immersion. Hence plated goods are now sought all over the world, and, if fairly used, are nearly as durable as silver itself. Of this material, dinner and dessert services have been manufactured from 50 to 300 guineas, and breakfast sets from 10 to 200 guineas, as sold on the spot.
"At Sheffield are actually cast and finished, most, if not all, the parts of grates sold as their own make by the London furnishing ironmongers. Their names are placed on them, but, in truth, [pg 413] they merely put the parts together. I saw in Messrs. Picklay's rooms superior castings for backs of grates, little inferior in delicacy to plaster of Paris; and for grates connected with one of these patterns, I was told 100 guineas each was lately paid by a northern squire. Grates with folding doors are made here as well as at Chesterfield. The doors are in half heights, so as to serve two purposes, and grates so supplied sell for about two guineas extra. Mr. Picklay has brought the kitchen range to great perfection. With one fire he roasts, boils with water and steam, and bakes. Economy and completeness were never more usefully combined; and a public establishment in Sheffield is fitted with one which has cooked a dinner complete for above three hundred persons. It cost nearly £300, but such grates for small families may be had at ten guineas.
"The mercantile part of the Sheffield trade is performed chiefly by travellers, but the principal shops in London deal directly with the manufacturers here. To humour public prejudice in regard to "Town make," as it is called, and to serve as an advertisement for various retailers in London and other large towns, their connexions in Sheffield keep steel brands, with which their names are placed on the articles, and they thereby pass with the public as the real manufacturers. I saw in different workshops, in Sheffield, the steel brands of our famous town makers, and the articles in wholesale quantities packing up to meet the demand in London for "real town made." This is a standing joke at the expense of cockney credulity among the Sheffield cutlers.
"Sheffield is noted for the manufacture of superior files; and many anecdotes are told of the artifices which have been made use of to aggrandize or to repudiate the celebrity of the marks of some well-known makers.
"In Sheffield generally the workmen get from 20s. to 24s. per week. Dry grinders get £2, and some £5 or £6, and these high wages are paid as an equivalent for the shortness of life. Many women are employed as filers, burnishers, polishers, finishers, &c. &c.; and they get from 6s. to 12s. per week.
"Very fine cutlery is manufactured by Mr. Crawshaw. I saw in his warehouse all those elegant patterns of pen-knives which, in the best shops of London, Bath, &c. excite so much admiration. His lobster knives, with four or more blades, on slit springs, with pearl and tortoiseshell handles, are the most perfect productions of British manufacture. His pen-knives with rounded or beveled backs, to turn in the quill and shave the point, are simple and effective improvements. He showed me plain pocket-knives so highly finished, that the first cost is 38s., yet so deceptive is cutlery, that I might have preferred others which I saw at only 7s. or 8s. It is the same in regard to the scissors of Champion and Son,—articles at two or three guineas did not appear to my uninstructed eye worth more than others at a few shillings; yet in all these high priced articles, nearly the whole cost is in workmanship, and there are but few workmen who can produce them. At the same time, Mr. Crawshaw deals in pen-knives at 5s. per dozen, and Mr. Champion in scissors at 2s. or 3s. per dozen.
"The novelties and curiosities in this way are extremely numerous, and the makers and inventers are as modest and communicative as they are original and ingenious. Thus a knife an inch long, weighing eight pennyweights six grains, containing seventy odd blades and instruments, cost £30 in making: scissors the eighth of an inch long, twenty-five of which weigh but a grain, sold at 3s. per pair: a knife, mounted in gold and pearl, containing thirty blades, is valued at £30; pocket-knives with twenty-six parts are sold at six guineas; the very best two blades mounted with pearl and gold, made by Crawshaw, are in common sale at two guineas in Sheffield. Messrs. Champion are esteemed the best makers of scissors; and ladies' working scissors, in general commerce, are finished and mounted as high as five or ten guineas. The best pocket-knives are made by Crawshaw, and fetch, in mounting, from two to five guineas. He is also the general maker of what are called the 'best town made.' I may here add, that Messrs. Champion can make a single set of table knives and forks, the fair market price of which would be 100 guineas.
"The mechanical ingenuity of Mr. Crawshaw has also been displayed in the construction of AN ORRERY consisting of at least 1,000 wheels, which, by a single winch, turns all the planets in their respective periods; and also the whole of the satellites, including those of Herschell. This orrery, perhaps the completest in the world, was made in all its details by this gentleman, and, in its wheel-work, is an astonishing production.
"One of the wonders of Sheffield is its Grinding Establishments. To aid [pg 414] the grinders, companies have erected very spacious buildings divided into small rooms, and provided the whole with steam engines. The rooms are then let out by the month to master grinders; and at properly adjusted grindstones in each room I saw every variety of grinding, sharpening, and polishing. The finest work is polished by hand, and in this slavery I saw the delicate hands of the superior sex solely employed. The payment is trifling; but I was told that the hand of woman is the softest, most pliable, and most accommodating tool which has yet been discovered for conferring the finest polish on the refractory substance of steel. Can we wonder at its effect in softening the ruggedness of the other sex, and how hard must be the heart of that man which does not yield to an influence which subdues even the hardness of steel.
"The manufacture of spectacles, telescopes, microscopes, etc. is carried on to a great extent in Sheffield. Above five gross per day are ground of convex and concave glasses in one shop. Concave basins cast in iron of the radii of curvature of proposed lenses are fixed in rows on a frame, and rubbed with water and emery. A concentric convex basin is then covered with round pieces of plate glass fixed with pitch; and the convex stir face, with its glass pieces, is then turned and wabbled in the concave basin by steam power. In this manner from six to twelve dozen glasses are ground at once by one basin working within the other on an eccentric axle which wabbles the inner basin while it is revolved. Of course, in time, i.e. in eight or ten hours, the glasses are so abraded, that the outside of one basin exactly fits the other, and the lenses between are of the true curvature. They are then knocked off the pitch; turned and worked on the other side, on the second day; cleaned with spirit of tar, rounded or clipt with blunt scissors, and fitted in spectacle frames or tubes. In Mr. Cutt's factory I saw twenty-six of these basins for spectacles, and about eighteen for telescopes and microscopes; several being at work."
"The Sheffield trades require and promote the Fine Arts in many ways. Chantrey was a carver and gilder here, and many persons in Sheffield were his first patrons, when he began to model. He was a native of Norton, where his parents still reside, and his first youthful employment was that of bringing milk to the town on asses, as is the present custom. At present, Mr. Law is an exquisite modeller in wax; and there are some ladies who copy the best pictures with a degree of taste and perfection which is astonishing. I allude particularly to those of Miss Green, of Westville House, and Miss Sambourne, at Highfield Green. Then this district possesses a treasure in Mr. Cowen, of Rotherham, whose merit as a landscape painter, has recommended him to the zealous patronage of Earl Fitzwilliam and the Duke of Devonshire. I confess I have never seen more exquisitely finished and more poetical productions."
"The Shrewsbury Hospital, at Sheffield, has lately been rebuilt in an improved situation, by Messrs. Woodhead and Hurst, of Doncaster. It accommodates eighteen aged men and eighteen women in a very convenient manner. It has been liberally supported by the present Duke of Norfolk, and is managed by trustees of his nomination. The men are allowed 10s. per week, and the women 8s. There is also another hospital, founded by a Mr. Hollis, a Sheffield cutler; as a provision for sixteen cutlers' widows, who besides habitations, receive 7s. per week, coals, and a gown every two years.
"In conclusion I have assembled some miscellaneous facts. Sheffield parish is ten miles by three. The Park of 2,000 acres was inclosed in Queen Anne's time.
"The Duke of Norfolk is Lord of the Manor, from his ancestors the Lovetots, Furnivals, Nevilles, Talbots, and Howards.
"Roger de Busli had 46 manors in Yorkshire, and in Nottinghamshire and Derbyshire 179.
"The Cutlers' Company was incorporated 21st James I.—The cutlers are 8,000 or 10,000 in number.
"In 1751, the first stage-wagon went from Sheffield to London. In 1762, the first stage-coach.
"In 1752, the plated manufacture began.
"In 1770, the first bank was opened.
"In 1786, the first steam-engine grinding-wheel was established.
"The casting or melting of steel began 60 years ago, till which time Swedish bar-steel was used.
"There are iron-forges near every Roman station, and Abbey Dale is full of cinders from smelting, with apertures to windward to serve as blasts.
"Beds of scoriae found in the parish, on which trees grow, and in old pleasure [pg 415] parks.—Roman coins are also found in scoria.—A quarry of stone at Wincobank Hill, contains fossilized vegetables, chiefly calamites. They are succulent, and of the bamboo family. In the coal districts, branches and trunks of trees are found; and Mr. Rhodes took out of solid stone, a fossil post of walnut wood. South-east of Tickhill, is an accumulation of subterranean trees, in black earth, mixed with shells and rounded stones.
"It is believed at Sheffield, that the executioner of Charles I., was a person of the name of William Walker, a native of Darnall, near Sheffield. Such was the tradition at his native place. He died at Darnall in 1700 and was buried in Sheffield church, where there was a brass plate to his memory. It is certain that a Walker, was one of the masks, and that this Walker was an active partizan: but he was a man of learning, and wrote some tracts on mathematics and politics.
"Dr. Buchan, began his career as a Scotch physician at Sheffield, and actually wrote his famous 'Domestic Medicine,' in the house at the south corner of Hartshead, in which for many years has resided Mr. J. Montgomery."
The varied and attractive character of our extract is the best plea for its length; but reading like this never tires.—-Sir R. Phillips' Personal Tour.
A snapper up of unconsidered trifles.
SHAKESPEARE.
At St. Lawrence, October 13, 1828, wind S.W. the atmosphere was filled with smoke, which, with intervening clouds, intercepted the sun's light, so as to require the use of candles several times during the day. The water which fell in the afternoon and evening was so much affected by the smoke as to be bitter to the taste.
When the art of distilling spirits, generally attributed to Raymond Lully, was discovered, the secret of longevity was supposed to have been brought to light, the mercurius volatilis to be at length fixed, and the pernicious product received the name of aqua vitae—liquor of life; "A discovery concerning which," says a learned physician, "it would be difficult to determine, whether it has tended most to diminish the happiness, or shorten the duration of life. In one sense it may be considered the elixir of life, for it speedily introduces a man to immortality!"
C.J.T.
Is manufactured in great abundance in Paris from the bones of butchers' meat. At one of the hospitals upwards of 1,000 basins of soup are furnished daily.
Are remarkable for the extraordinary size of their horns, some of which are four feet long, seven inches in diameter near the head, and hold ten quarts.
Paul Spencer exhibits the following distich on his door, in Glasgow:—
"Entertainment here for all that passes,
Horses, mares, mules, and asses."
C.J.T.
According to a calculation recently made, there are 103 canals in Great Britain—extending 2,682 miles, and formed at an expense of thirty millions sterling.
C.J.T.
"Do you know what made my voice so melodious?" said a celebrated vocal performer, of awkward manners, to Charles Bannister. "No," replied the other. "Why, then, I'll tell you: when I was about fifteen, I swallowed, by accident, some train oil." "I don't think," rejoined Bannister, "it would have done you any harm if, at the same time, you had swallowed a dancing-master!"
CHEAP and POPULAR WORKS published at the MIRROR OFFICE in the Strand, near Somerset House.
The ARABIAN NIGHTS ENTERTAINMENTS. Embellished with nearly 150 Engravings. In 6 Parts, 1s. each.
The TALES of the GENII. 4 Parts, 6d. each.
The MICROCOSM. By the Right Hon. G. Canning. &c. 4 Parts, 6d. each.
PLUTARCH'S LIVES, with Fifty Portraits, 12 Parts, 1s. each.
COWPER'S POEMS, with 12 Engravings, 12 Numbers, 3d. each.
COOK'S VOYAGES, 28 Numbers, 3d. each.
The CABINET of CURIOSITIES: or, WONDERS of the WORLD DISPLAYED 27 Nos. 2d. each.
BEAUTIES of SCOTT, 36 Numbers, 3d. each.
The ARCANA of SCIENCE for 1828. Price 4s. 6d.
GOLDSMITH'S ESSAYS. Price 8d.
DR. FRANKLIN'S ESSAYS. Price 1s. 2d.
BACON'S ESSAYS Price 8d.
SALMAGUNDI. Price 1s. 8d.
Footnote 2: (return)For the remainder of the Extract, &c. see MIRROR, vol. xii. p. 151. Only a few days since we saw recorded an instance of enthusiasm in the study of astronomy, which will never be forgotten. We allude to Mr. South's splendid purchase at Paris; yet all the aid he received was some trifling remission of duty!
Footnote 3: (return)See the Propagation of the Insect in Spain, MIRROR, vol. xii. and an attempt to naturalize the same at the Cambridge Botanical Garden, page 217, of the present volume.
Printed and Published by J. LIMBIRD, 143, Strand (near Somerset House,) London; sold by ERNEST FLEISCHER, 626, New Market, Leipsic, and by all Newsmen and Booksellers.